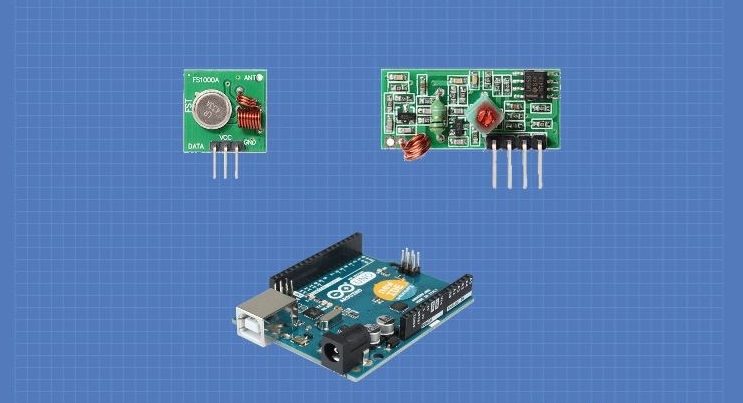
Selecting the right RF Module is crucial for successful IoT deployments. Sub-GHz and 2.4GHz modules dominate the market, each offering unique advantages. Engineers must evaluate project requirements, including range, power consumption, data rate, and network environment. Using the correct frequency ensures reliable communication and optimizes device performance. For instance, smart agriculture or industrial IoT devices rely heavily on extended range and low energy use. By contrast, high-density networks in smart homes prioritize data throughput and interference handling. Understanding these differences early helps prevent costly redesigns and improves long-term operational efficiency.
Signal Range and Penetration Capabilities
Sub-GHz frequencies, typically 315 MHz, 433 MHz, 868 MHz, and 915 MHz, offer a more extended range than 2.4 GHz RF Modules. They can penetrate walls, foliage, and industrial obstacles more effectively, making them ideal for outdoor and expansive indoor applications. In rural agricultural IoT setups, Sub-GHz modules maintain stable communication over several kilometers. On the other hand, 2.4GHz modules excel in short-range, high-density environments. While 2.4GHz signals offer higher data rates, their range is often limited to tens of meters in obstructed areas. Selecting the right frequency depends on deployment scale and environmental challenges.
Power Consumption Considerations
Power efficiency is a critical factor for battery-operated IoT devices. Sub-GHz RF Modules typically consume less power during transmission due to lower frequency propagation characteristics. This allows devices to operate for months or even years on a single battery. Low-power Sub-GHz networks are widely used in smart meters, environmental sensors, and remote monitoring devices. In contrast, 2.4GHz modules, while capable of faster communication, often require more frequent energy replenishment. Developers must weigh battery life requirements against data throughput when deciding which RF Module to integrate.
Data Rate and Throughput
2.4 GHz RF Modules support higher data rates than Sub-GHz options. Modules operating at 2.4 GHz can easily reach tens of megabits per second, making them suitable for real-time data transfer and multimedia applications. Sub-GHz modules, while more energy-efficient and longer-range, typically support lower data rates, often less than 500 kbps. For example, environmental IoT sensors transmit small packets intermittently, making Sub-GHz sufficient. Conversely, IoT applications involving video streaming, live monitoring, or rapid data analytics benefit from the speed advantages of 2.4GHz modules.
Network Density and Interference Management
High-density networks challenge RF communication. 2.4 GHz frequencies are crowded by Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and other devices, potentially causing interference. Effective interference management, channel hopping, and robust protocols are essential for reliable performance. Sub-GHz bands generally face less congestion, providing more stable connectivity in dense industrial or rural deployments. Case studies of innovative building projects show that Sub-GHz RF Modules maintain data integrity and reduce packet loss when multiple devices operate simultaneously.
Regulatory and Regional Considerations
Regulatory compliance varies by frequency band and region. Sub-GHz frequencies vary globally; for instance, 868 MHz is standard in Europe, while 915 MHz is common in North America. Developers must ensure chosen RF Modules meet local certification standards. 2.4GHz modules are widely available and subject to fewer regulatory constraints, simplifying international deployment. Understanding these regulatory factors early prevents legal complications and ensures uninterrupted IoT operation across different regions.
Cost Implications and Component Availability
Component cost and availability influence design decisions. Sub-GHz RF Modules are often slightly more expensive due to lower production volumes, but they reduce system-level costs through a more extended range and energy savings. 2.4 GHz modules benefit from mass production, reducing per-unit costs. However, additional infrastructure may be required to maintain range and reliability in larger deployments. Evaluating the total cost of ownership—including device, network, and maintenance costs—helps engineers choose the most cost-effective RF Module for their IoT project.
Choosing the Right RF Module for Your IoT Project
Selecting between Sub-GHz and 2.4GHz RF Modules requires a balanced assessment of range, power consumption, data rate, network density, regulatory compliance, and cost. Sub-GHz modules excel in long-range, low-power applications with fewer interference challenges, while 2.4GHz modules provide high-speed connectivity for dense environments. Real-world deployments demonstrate that aligning frequency choice with project requirements optimizes performance, reliability, and total operational efficiency.